Featured Quizzes
User Quizzes
Create Quiz
Data and Charts
Badges and Games
About JetPunk
JetPunk Shop
Dark Mode
Texas Waste Water Treatment Final Exam Review
Take the test..... duh.......
Study questions for the class C waste water license.
Info source: TEEX infrastructure training & safety institute waste water treatment resource book Appendix G 2023.
Rate:
Last updated: February 23, 2024
You have not attempted this quiz yet.
More quiz info >>
| First submitted | January 17, 2024 |
| Times taken | 17 |
| Average score | 70.0% | Report this quiz | Report |
10:00
The quiz is paused. You have remaining.
Scoring
You scored / = %
This beats or equals
% of test takers
also scored 100%
The average score is
Your high score is
Your fastest time is
Keep scrolling down for answers and more stats ...
1.
The purpose of the microorganisms that are present in biological treatment processes
is to ________.
provide the operator with pets
✓
add gases to the treatment plant
✓
remove the bacteria in raw wastewater
✓
trap and consume contaminants in wastewater
✓
In secondary treatment, microscopic living creatures called microorganisms remove additional contaminants from the wastewater. Conditions are purposely created that favor the growth and reproduction of treatment microorganisms. These organisms trap and consume waste, using contaminants in wastewater as their food supply. After these organisms are later removed as biological solids, the wastewater will be less contaminated. NOTE: The purpose of the microorganisms.... is to BE the biology in "biological treatment" they eat things and turn them into other things that are more easily removed than the original contaminants.
2.
The extent of treatment required for a waste discharge depends on ________.
the final use of the sludge
✓
what the community can afford
✓
the treatment plant disinfection method
✓
water quality standards set for the receiving stream
✓
National, state, and local governments set the standards for treatment. These requirements depend on treatment plant location, the water quality standards set for the receiving stream, and the amount and final use of the effluent. Different treatment plants have different requirements. NOTE: the idea is not to make fresh drinking water but to process waste water to the point that it matches or exceeds the quality of the water way it will be discharged into.
3.
Which type of activated sludge process must have primary clarification?
Extended air
✓
Conventional
✓
Complete Mix
✓
Contact Stabilization
✓
See Table 8.10: Conventional Activated Sludge for details. complete mix and contact stabilization may or may not use primary clarification. and extended air does not use it at all.
4.
Whoever violates any part of the ________ or any permit or order of the TCEQ can be fined up to $25,000 per day per violation.
water code
✓
wastewater code
✓
40 CFR Part 403
✓
regulatory guidance
✓
If the TCEQ finds that a violation of the Water Code or of a TCEQ rule, permit, or order occurred, the agency may issue a conclusive report and recommend a penalty (usually a TCEQ administrative penalty). The TCEQ may assess administrative penalties up to $25,000 per day for each violation.
5.
Septic wastewater ________.
is gray with a slight fecal order
✓
is black and has very little odor
✓
has dissolved oxygen present with visible floating solids
✓
is the result of bacterial decomposition in the absence of oxygen
✓
Septic wastewater is a dark color, has a disagreeable odor, and contains no DO. The floating material is hard to see, and gas bubbles are seen rising to the surface. The change from fresh to septic is caused by bacterial action, as anaerobic bacteria consume organic materials and produce organic acids and odorous gases.
6.
BOD is a measure of ________.
algae population
✓
amount of DO present
✓
chemical oxygen demand
✓
amount of oxygen used up
✓
Biochemical oxygen demand (BOD, or specifically BOD5 when referring to the test) is the quantity of dissolved oxygen, expressed as milligrams per liter, required (depleted or used up) to partially stabilize the decomposable organic matter in a waste stream by chemical and biological action over 5 day period of time at 20°C.
7.
Too high a velocity in a grit chamber can result in ________.
septic wastewater
✓
increase in volatile solids
✓
settling of dissolved solids
✓
excess grit in the primary clarifier
✓
If the velocity is too high, the grit will be carried over into the primary clarifier; if the velocity is too low, some suspended organic solids may settle out with the grit and become septic in the chamber.
8.
The moisture content of sludge from a primary clarifier should be which of the following?
4%–6%
✓
90%–91%
✓
94%–96%
✓
None of the above
✓
while this IS a question in module 5 review the following sentence does not appear until module 11. "Primary sludge has a fecal odor and is from 94% to 96% moisture." Module 5 has only this to say "The dry weight solids content (of primary sludge) is 4% to 6%..."
9.
Bacteria may be classified by which of the following?
Shape
✓
Oxygen needs
✓
Temperature and metabolism
✓
All of the above
✓
Bacteria, being very small and indistinct, are difficult to identify. They are often put into categories according to size and shape, oxygen needs, temperature requirements, food needs (metabolism), and the by-products they produce.
10.
Which type of bacteria adapts best to changing environmental oxygen conditions?
Aerobic
✓
Anaerobic
✓
Facultative
✓
Pathogenic
✓
Facultative bacteria are microorganisms that can use dissolved oxygen (DO) OR oxygen obtained from food materials such as sulfate or nitrate ions, and some can respire through glycolysis. These bacteria can live under aerobic, anoxic, or anaerobic conditions.
11.
A contact stabilization activated sludge plant has a fast settling sludge and high amounts of pin floc leaving the clarifier. One way to correct this problem is to ________.
reduce wasting rates
✓
increase the RAS flow
✓
increase the sludge age by wasting less
✓
increase the F/M ratio by wasting more
✓
"Fast settling sludge and high amounts of pin floc leaving the clarifier" indicates old sludge that has been more than sufficiently processed staying in the system. wasting is how we get rid of the stuff we are done with before final dewatering, stabilization, and disposal. the question seems to be specifically referencing Table 8.19: Troubleshooting Guide for Activated Sludge Systems: Secondary Clarifier (Continued) which lists this as the proper corrective action: "Check F/M, MCRT, or sludge age and increase wasting rates by no more than 10% per day to return to optimum conditions."
12.
Testing of mixed liquor indicates the MLSS is 3,500 mg/L, and the settling test shows that a 1,000 mL sample settles to 350 mL after 30 minutes. What is the SVI and sludge quality?
80 and good
✓
100 and good
✓
100 and bulking
✓
400 and bulking
✓
The "good", "bulking", and "too compacted" quality descriptions in this question refer entirely to the calculated Sludge Volume Index(SVI) numbers. SVI helps the operator know if the sludge is bulky. Numbers between approximately 70 and 150 are typical for healthy activated sludge. Above 150, the sludge gets increasingly bulky and harder to settle. Below 70, the floc does not clump adequately and more suspended solids remain entrapped by the floc as it settles rapidly. SVI = (30 minute settled volume (mL) / MLSS (mg/L)) X 1000 (converts mL to L and mg to g)) = (350mL / 3,500mg/L) X 1000 = 0.1 X 1000 = 100!
13.
Which of the following materials should not go onto a trickling filter?
Colloidal solids
✓
Dissolved solids
✓
Finely divided solids
✓
Large suspended solids
✓
Wastewater applied to a trickling filter usually has had the large solids removed in a primary clarifier. Only the finely divided, suspended solids, the colloidal solids, and the dissolved solids remain.
14.
Which of the following is true of trickling filter media?
Must hinder recirculation
✓
Must be crushed limestone
✓
Must be durable and provide enough surface area for bacterial growth
✓
All of the above
✓
The main purpose of the media is to provide a surface on which the microorganisms can grow. Media must be durable because treatment plants are designed for many years of service. Various media materials have been used, including stone, slag, ceramics, coal, and redwood blocks, or slats. Synthetic materials, such as molded plastic, also have come into use. They are lightweight and easy to handle, allowing greater filter depth without excess weight on underdrains and floor. They double the surface area exposed for the growth of film and their voids clog less often than those of stone filters.
15.
Which activated sludge process has 20+ hours detention time in the aeration basin?
Conventional
✓
Extended Air
✓
Complete Mix
✓
Contact Stabilization
✓
See Table 8.11: Extended Aeration
16.
Rotating biological contactors may be ________.
rotated at about 3.5 rpm
✓
heated by an electric motor
✓
considered primary treatment units
✓
driven by electric motors or trapped air
✓
Normally, the basins will function with the discs in continuous operation. Wastewater from the primary clarifier enters the head of the RBC through two influent pipes. The influent wastewater displaces water and sloughed solids into the effluent channel leaving the basin. The displaced water then flows through transfer pipes to the final clarifier for further treatment. The discs are slowly rotated at a rate of 1.0 to 1.5 rpm or about 1 ft./sec. peripheral speed. Each unit is driven either by a motor with a gear reducer or by air trapped in air cups. When driven by a motor, the drive assembly on each drum or disc is powered by an electric motor operating at 1,200 rpm. When driven by air, air headers below the disc allow air to fill air cups installed on the periphery of the disc. The air buoyancy turns the disc.
17.
Wastewater stabilization ponds will effectively reduce ________.
pH
✓
odors
✓
BOD and bacteria
✓
total suspended solids
✓
All pond systems are capable of reducing biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), bacteria, and other biodegradable materials.
18.
The organic loading on wastewater stabilization ponds should not exceed ________.
20 lb. BOD/acre/day
✓
30 lb. BOD/acre ft./day
✓
35 lb. BOD/acre/day
✓
35 lb. BOD/acre ft./day
✓
Organic loading on wastewater stabilization ponds (when used for secondary treatment) is based on the total surface area of all ponds and should not exceed 35 lb. BOD5/acre/day. Detention times are above 30 days. The loading on the initial pond should not exceed 75 lb. BOD5/acre/day.
19.
Which of the following should digester gas contain?
1%–5% carbon dioxide
✓
15%–30% nitrogen
✓
65%–75% methane
✓
None of the above
✓
The gas composition in a well-run digester will be about 65%–75% methane and 25%–35% carbon dioxide.
20.
The moisture content of sludge transported to a municipal landfill should be less
than ________.
20%
✓
40%
✓
60%
✓
80%
✓
For sludge to be disposed of in a sanitary landfill, it must first be dewatered to prevent contamination of ground and surface water. In addition, the solids content must amount to at least 20% of the total.
21.
Which of the following is formed when gas chlorine is added to water?
H2S
✓
HCl
✓
HOCl
✓
HCL AND HOCL
✓
When chlorine is added to water, it forms a mixture of hydrochloric acid (HCl) and hypochlorous acid (HOCl). Hydrochloric acid is not a disinfectant. The hypochlorous acid compound ionizes into H+ and OCl. The degree of ionization depends on the pH. Cl2 + H2O HOCl (Hypochlorous) + HCl (Hydrochloric) Hypochlorous acid is extremely effective as a disinfectant, but the hypochlorite ion (OCl) is not. At a pH of 4 or 5 the HOCl concentration is almost 100%. As the pH increases, the percent HOCl decreases, thus decreasing its disinfecting capabilities. At a pH of 7.0 the HOCl concentration is about 70%–80% (Figure 12.2). Most wastewater effluents fall in this range. NOTE: the book mentions nothing about CaCl2 (calcium chloride) being formed when adding gaseous chlorine to water and per the snippet i started with the answer should be HCL AND HOCL but that is not the answer given and is not apparently going to be the answer you see on the test for your license....
22.
The TCEQ requires a chlorine residual of at least ________.
0.5 mg/L residual at the outfall
✓
1.0 mg/L residual at outfall
✓
1.0 mg/L residual after 20 minute contact
✓
2.0 mg/L residual after 20 minute contact
✓
Where chlorination is utilized, any combination of detention time and chlorine residual where the product of chlorine (Cl, mg/L) x Time (T, Minutes) equals or exceeds 20 is satisfactory provided that the minimum detention time is at least 20 minutes at peak flow and the minimum residual is at least 1.0 mg/L. The maximum chlorine residual in any discharge shall in no event be greater than 4.0 mg/L, or that necessary to protect aquatic life.
23.
Total suspended solids are ________.
sometimes in solution
✓
greater than total solids
✓
determined by filtration
✓
determined by heating to 550°C
✓
Total solids, or total residue (TR), are all the solids present in wastewater regardless of form or composition. Total solids consist of suspended and dissolved solids so neither will be "greater than the total solids". If for some reason you think suspended or dissolved solids are not in a solution i would ask you what you think they are suspended or dissolved IN while looking at you funny. Oh yeah, the book also defines suspended and volitile solids thusly: Total suspended solids (TSS) are those that can be filtered out. Volatile suspended solids (VSS) is the amount of TSS that is volatile. VSS is determined by burning the TSS sample at 550°C, which burns off all of the organics.
24.
A good sludge volume index should range from ________.
50 to 75
✓
70 to 90
✓
95 to 125
✓
150 to 200
✓
SVI helps the operator know if the sludge is bulky. Numbers between approximately 70 and 150 are typical for healthy activated sludge. Above 150, the sludge gets increasingly bulky and harder to settle. Below 70, the floc does not clump adequately and more suspended solids remain entrapped by the floc as it settles rapidly. SVI = (30 minute settled volume (mL) / MLSS (mg/L)) X 1000 (converts mL to L and mg to g))
25.
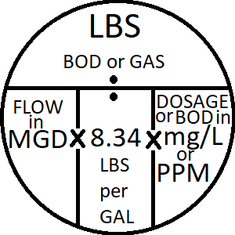
A POTW has a flow of 3.5 MGD and an influent BOD of 220 mg/L. Find the pounds of
BOD in the influent.
1,223 lb.
✓
6,422 lb.
✓
7,225 lb.
✓
8,965 lb.
✓
Lbs BOD = MGD X 8.34 lbs/gal X mg/L = 3.5MGD × 8.34lbs/gal × 220mg/L = 6,421.8lbs! NOTE: all you get for these problems will be the TLDR section of the explanation you would have seen in earlier modules. if you want a better explanation i recommend visiting those.
26.
What is the detention time in hours of a tank 50 ft. long, 25 ft. wide, and 10 ft. deep, with a flow of 2 MGD?
1.12 hrs
✓
1.64 hrs
✓
2.28 hrs
✓
2.44 hrs
✓
DThrs = BasinCapacity gal / fill rate gph = (L X W X D X 7.48 gal/ft^3)gal / ((MGD X 1,000,000) / 24hrs)gph = (50ft × 25ft × 10ft × 7.48gal/ft^3)gal / ((2MGD X 1,000,000) / 24)gph = 93,500gal / 83,333gph = 1.12hrs!
27.
A treatment plant has two primary clarifiers. Each has a diameter of 40 ft. and a depth of 12 ft. If the design flow is 1.2 MGD, find the surface loading on each clarifier in
gal./ft.2/day. Assume the flow is equally split between the two clarifiers.
325 gal./ft.2 /day
✓
478 gal./ft.2/day
✓
650 gal./ft.2/day
✓
956 gal./ft.2/day
✓
Surface loading = flow / clarifier surface area = ((MGD X 1,000,000) / 2 clarifiers)gpd / (3.14 X R X R)ft^2 = ((MGD X 1,000,000) / 2)gpd / (3.14 X (D / 2) X (D / 2))ft^2 = ((1.2 X 1,000,000) / 2)gpd / (3.14 X (40/2) X (40/2))ft^2 = (1,200,000 / 2)gpd / (3.14 X 20 X 20)ft^2 = 600,000gpd / 1256ft^2 = 477.7gal/ft^2/day = 478gal/ft^2/day!
28.
A standard rate rock trickling filter is 120 ft. in diameter and 8 ft. deep. What is the
hydraulic loading in MG per acre per day if 1.0 MGD is treated?
2.15 MGAD
✓
2.70 MGAD
✓
3.25 MGAD
✓
3.85 MGAD
✓
MGAD = flow in MGD / area of trickling filter in acres = 1MGD / ((3.14 X 60 X 60)ft^2 / 43,560ft^2/acre)acre = 1MGD / (11,304ft^2 / 43,560ft^2/acre) = 1MGD / 0.2595acres = 3.85 MGAD!
29.
What will be the detention time in days in a pond that is 850 ft. long, 250 ft. wide with an
average depth of 4 ft. that is receiving a flow of 0.2 MGD and has a net evaporation loss of 8 in. per 30 day month?
30.45 days
✓
36.70 days
✓
38.65 days
✓
40.20 days
✓
DTdays = PondCapacitygal / net volume gained per daygal/day = (Lft X Wft X Dft X 7.48gal/ft^3)gal / ((MGD X 1,000,000)gpd - (EvapLoss / 30days)gpd) = (850ft X 250ft X 4ft X 7.48gal/ft^3)gal / ((0.2MGD X 1,000,000)gpd - ((Lft X Wft X (Din / 12)ft X 7.48gal/ft^3)gal / 30days)gpd) = 6,358,000gal / (200,000gpd - ((850ft X 250ft X (8in / 12)ft X 7.48gal/ft^3)gal / 30days)gpd) = 6,358,000gal / (200,000gpd - (1,058,607gal / 30days)gpd) = 6,358,000gal / (200,000gpd - 35,287gpd) = 6,358,000gal / 164,713gpd = 38.6days!
30.
If 200 lb./day of gas chlorine is added to 2.8 MGD, what is the dosage in mg/L?
5.9 mg/L
✓
6.5 mg/L
✓
7.8 mg/L
✓
8.6 mg/L
✓
Dosagemg/L = lbsBOD / (MGD X 8.34lbs/gal) = 200lb/day / (2.8MGD X 8.34lbs/gal) = (200 / 23.352) = 8.56mg/L!
Comments
No comments yet
New and Popular
Save Your Progress
Texas Waste Water Treatment Study Guide
Quiz series by Mandaris
Copyright H Brothers Inc, 2008–2024
Contact Us | Go To Top | View Mobile Site
