Featured Quizzes
User Quizzes
Create Quiz
Data and Charts
Badges and Games
About JetPunk
JetPunk Shop
Dark Mode
Texas Basic Waste Water Operations Final Exam Review
Take the test..... duh.......
Study questions for the class D waste water license.
Info source: TEEX infrastructure training & safety institute basic waste water operations resource book Module Final Exam 2023.
Rate:
Last updated: November 9, 2023
You have not attempted this quiz yet.
More quiz info >>
| First submitted | November 9, 2023 |
| Times taken | 9 |
| Average score | 80.0% | Report this quiz | Report |
10:00
The quiz is paused. You have remaining.
Scoring
You scored / = %
This beats or equals
% of test takers
also scored 100%
The average score is
Your high score is
Your fastest time is
Keep scrolling down for answers and more stats ...
1.
Each person contributes about ________ lbs of BOD daily.
0.17
✓
1.7
✓
17
✓
0.71
✓
The population equivalent is defined as 0.17 pounds of BOD a human produces per day. The population equivalent factor is used to mathematically determine the number of humans (population) contributing waste. Additionally, if the population factor is known, the BOD can be mathematically determined.
2.
A ladder must be within ________ feet of anyone in the trench.
25
✓
24
✓
23
✓
22
✓
The ladder must extend three feet above the trench and be secured. Ladders must be within 25 feet of trench workers and not more than 50 feet apart.
3.
Examples of point source discharges are ________.
stormwater drainage from industry and urban areas
✓
seepage from septic tanks and drain fields
✓
municipal, industrial, and agricultural wastewater treatment facilities
✓
all of the above
✓
Point-source discharges come from pipes or concrete ditches that are monitored, controlled, and inspected. Some examples include municipal, industrial, agricultural, and wastewater treatment facilities, as well as controlled stormwater discharges from municipalities and industry.
4.
Protecting Texas water from contamination requires ________ of wastewater.
collection and transportation to treatment
✓
treatment that removes contaminants
✓
processing and disposal of solids
✓
all of the above
✓
The proper handling of wastewater requires collection and transportation of wastewater to treatment facilities, treatment of contaminants, and processing of solids removed from wastewater.
5.
The normal operator controls on an activated sludge process are ________.
RAS, WAS, and DO
✓
aeration basin and clarifier design
✓
types of organisms in the process
✓
all of the above
✓
Factors influencing the activated sludge process are called control parameters. Five control parameters are Dissolved Oxygen (DO), solids quantity, solids quality, return rate, and wasting rate. An activated sludge plant will not operate effectively without these operator controls. Operators control aeration and mixing by maintaining the efficient use of the aeration equipment. Return activated sludge (RAS) rates may be controlled by adjusting pumping equipment or telescoping valves to achieve a desired rate of return. Operators may control wasting with timely removal of excess, dead, or inert solids from the system.
6.
Ponding on a trickling filter is caused by ________.
excessive zoogleal growth
✓
improper media
✓
poor primary treatment
✓
all of the above
✓
Ponding results from clogged filters caused by excessive zoogleal growth, debris, insects, snails, improper media, or poor primary treatment.
7.
Organic loading is the pounds per day of ________ per acre-feet or 1,000 cubic feet of
media.
BOD
✓
TSS
✓
DO
✓
RBC
✓
Hydraulic loading is the volume of water, including recirculation, applied to the filter in gallons per day/square foot (GPD/square foot) of media or million gallons per day per acre (MGD/acre) of media. Organic loading is in pounds of BOD per day per acre-foot or 1,000 cubic feet of media. An acre-foot is 1 surface acre (43,560 ft2 ) that is 1 foot deep.
8.
An ultrasonic flow monitoring device works on the principle of ________.
radar
✓
solar
✓
radio
✓
sonar
✓
Ultrasonic flow meters work with a weir, flume, or filled pipe, and use the principle of sonar. Sound from the unit bounces off or through the water and back to the receiver. The unit measures the round-trip time or change in sound and then computes the flow rate.
9.
The primary causes of wastewater stoppage are ________.
poor design and construction
✓
rain and dirt
✓
roots and grease
✓
customer abuse
✓
The primary causes of stoppage are roots and grease. Other factors include poor construction, public abuse, flushing disposable wipes, line failure, and flat grades. To prevent line stoppages and clogging, collection lines should be cleaned regularly.
10.
The pH scale ranges from ________ to ________.
1/14
✓
0/14
✓
7/14
✓
0/7
✓
pH measures acidity or basicity of a solution. The scale ranges from 0 to 14 with 7.0 being neutral. Acidic water has a pH below 7.0, and alkaline or basic water has a pH above 7.0. pH stands for potential hydrogen ion concentration.
11.
When an accidental discharge, bypass, or spill occurs, the discharger must notify the TCEQ within ________ hours.
24
✓
36
✓
48
✓
72
✓
§327.32. Reporting Requirements for Certain Accidental Discharges or Spills of Treated or Untreated Wastewater at Wastewater Treatment Facilities or Collections Systems. (b) Except as provided by subsection (c) of this section, all accidental discharges or spills of treated or untreated wastewater shall be reported within 24 hours of the occurrence. A written submission shall be provided to the executive direct within five days of the occurrence. The written submission shall contain a description of the accidental discharge or spill and its cause; the potential danger to human health or safety, or the environment; the duration of the accidental discharge or spill, including exact dates and times; if the cause of the accidental discharge or spill has not been corrected, the time it is expected to continue; and steps taken or planned to reduce, eliminate, and prevent reoccurrence, and to mitigate its adverse effects.
12.
An administrative penalty for discharge violations can be up to ________ per day.
$50,000
✓
$25,000
✓
$5,000
✓
$10,000
✓
To meet stream standards, the state issues permits for waste discharges. Permits have stricter limits when the effluent discharges into water used for drinking or swimming. Permits are stricter when a river or lake receives multiple discharges or large volumes of waste. The fine for polluting state water can be as much as $25,000 per day.
13.
When chlorine is used, the effective disinfectant is ________.
HCl
✓
HOCl
✓
H2SO4
✓
H2S
✓
When chlorine is mixed with water, hypochlorous and hydrochloric acids form: Cl2 + H2O -> HOCl (Hypochlorous) + HCl (Hydrochloic) ||| Hypochlorous acid (HOCl) is the free, chemically uncombined residual, and a powerful disinfectant. Because HOCl is an acid, it works well at low pH, but weakens as the pH increases.
14.
One surface acre of ponds provides treatment for about ________ people.
500
✓
300
✓
200
✓
none of the above
✓
One surface acre furnishes treatment for about 300 people. Organic loading of a stabilization pond is about 35 pounds of BOD per acre per day with a detention time of 30 days or more.
15.
Examples of waterborne pathogens are ________.
hepatitis A, typhoid, and flu
✓
cholera, dysentery, and cancer
✓
typhoid, cholera, and dysentery
✓
giardia, Cryptosporidium, and measles
✓
There are numerous waterborne diseases. These include the following: • Typhoid • Cholera • Paratyphoid • Dysentery • Poliomyelitis • Gastroenteritis • Giardiasis* • Cryptosporidiosis* • Hepatitis A (*Giardia and Cryptosporidium are chlorine-resistant microorganisms and are not inactivated at normal dosage and contact times.)
16.
When sludge in an Imhoff tank is near ________ inches of the slot, withdraw sludge.
14
✓
16
✓
18
✓
20
✓
When sludge is within 18 inches of the slot, withdraw sludge. Digested sludge is dark in color with a tarry odor. Do not withdraw more than 50% of the sludge at once. If compacted sludge or silt at the bottom of the riser pipe blocks sludge withdrawal, agitate the sludge with water through the riser pipe or stir the sludge inlet through the riser pipe with rods. After withdrawing sludge, fill the riser pipe with water to prevent sludge caking.
17.
A weir is an obstruction placed in a channel causing the water to ________.
back up
✓
pressurize
✓
evaporate
✓
run off
✓
A weir is an obstruction placed in a channel causing the water to back up. The depth of the water flowing over the weir determines the flow rate. Common weir designs are V-notch, rectangular, and Cipolletti.
18.
The most important problem prevented by monitoring or restricting industrial waste is
________.
sludge contamination
✓
worker exposure
✓
effluent pollutants
✓
wastewater fires
✓
Monitoring industrial waste prevents the following: • Worker exposure to chemical hazards (most important) • Interference with treatment • Sludge contamination • Pollutants in effluent • Explosions or fires Federal regulations require an industrial waste control program when flow exceeds 5 million gallons per day (MGD) or an industrial waste is regulated by federal standards (CFR, Title 40).
19.
Excavations ________ feet or deeper should be shored, shielded, or sloped.
3
✓
4
✓
5
✓
6
✓
Excavations that are 5 feet or deeper should be shored, shielded, or sloped. Cave-ins result from the following: • Dirt too near the trench edge • No shoring • Trench wall undercutting • Shoring failure
20.
The primary purpose of returning sludge in the activated sludge process is to have enough ________ in the aeration basin to match the food supply.
water
✓
microorganisms
✓
BOD
✓
DO
✓
The primary purpose of returning sludge is to have enough microorganisms in the aerator to match the food supply. Adjust return rates to produce the desired F/M ratio. Small plants often keep return rates constant. Large plants, particularly those with tapered aeration, can plug flow or step-feed aerators; adjust return rates throughout the day. Adjust return rates to maintain proper blanket depth. Keep the blanket in the bottom ¼ of the clarifier depth. If the blanket is too high or the mixed liquor is too thin, increasing the return rate may help.
21.
A simple method of determining when to waste from an activated sludge plant is the
________.
sludge volume index
✓
mixed liquor suspended solids
✓
30-minute settling test
✓
F/M ratio
✓
Activated sludge must be good quality to produce a clean effluent, low in BOD and TSS. Quality sludge is brown and has a slightly musty odor similar to wet dirt. There are several methods used to evaluate sludge: settling characteristics, settling test observations, sludge volume index, and microscopic examination. The 30-minute settling test (SV30) is simple and is a key indicator of good quality sludge. Test frequently on a well mixed, representative sample of mixed liquor. Allow the sample to settle for 30 minutes in a settleometer, graduated cylinder, or large beaker or jar (Figure 8.8). Record the results every five minutes. Although the 30-minute settling test is an useful method of determining when to waste activated sludge, other factors should also be used to determine when to waste excess solids from the system.
22.
Imhoff tanks are ________ story units with ________ compartments.
3/2
✓
3/3
✓
2/3
✓
2/2
✓
Imhoff tanks are two-story units with three compartments. The upper compartment is the settling tank. The lower compartment is the digester. The settling compartment provides detention time of about two hours. Gas vents alongside the settling tank are the third compartment. A trapped slot in the bottom of the settling compartment permits settled solids to pass into the digester, but prevents septic solids from rising into the settling compartment. Gas bubbles and septic solids are deflected into the gas vents by the slopping bottom of the settling tank.
23.
Aerobic digestion is an ________ process whereby the aerobic bacteria consume
themselves.
endothermic
✓
endangered
✓
endogenous
✓
endemic
✓
Aerobic digestion is an endogenous process. Endogenous means it is an internal process. When there is a lack of food, the bacteria consume themselves.
24.
In a well operated anaerobic digester, the methane gas content is about ________.
60-65%
✓
65-75%
✓
70-80%
✓
75-85%
✓
In the methane fermentation stage, anaerobic bacteria called methane formers convert the volatile acids into methane gas. Carbon dioxide (CO2) forms during all stages and should be 15–30% of the digester gases. In a well operated anaerobic digester, methane content is about 65–75%.
25.
Organic loading of a stabilization pond is about ________ pounds of BOD/acre/day with a detention time of at least ________ days.
30/30
✓
35/35
✓
30/35
✓
35/30
✓
Organic loading of a stabilization pond is about 35 pounds of BOD per acre per day with a detention time of 30 days or more.
26.
Gas chlorinator feed rates are indicated by the ________ in pounds per day.
residual
✓
injector
✓
rotameter
✓
controller
✓
Gas units connect to cylinders or manifolds and use vacuum produced by the injector or ejector to suction chlorine into a water stream. The rotameter (rate indicator) indicates feed rates in pounds/day or grams/hour. The flowrate controller (rate valve) sets the feed rate.
27.
How many square feet are in the end section of a 24-inch wastewater pipe?
3.14 square feet
✓
3.85 square feet
✓
7.48 square feet
✓
8.34 square feet
✓
TLDR: Area = Pi X r^2 = (3.14 X 12in X 12in) / (12in/ft X 12in/ft) = 3.14ft^2! ||| EXPLANATION: This question wants to know the cross sectional area of a 24in diameter pipe in square feet. To do this we multiply 3.14 by the radius squared to yeild the cross-sectional area of the pipe in in^2. (Area(in^2) = Pi X r^2 = Pi X r X r = Pi X (diameter / 2) X (diameter /2) = 3.14 X (24 / 2)in X (24 / 2)in = 3.14 X 12in X 12in = 452.16in^2) now that we have the area in square inches we need to convert that to square feet by dividing by the number of square inches per square foot. (Area(ft^2) = Area(in^2) / 144in^2/ft^2 = 452.16in^2 / 144in^2/ft^2 = 3.14ft^2!)
28.
How many cubic yards of dirt are removed from a trench 600 feet long, 4 feet wide, and
8 feet deep?
444 cubic yards
✓
533 cubic yards
✓
622 cubic yards
✓
711 cubic yards
✓
TLDR: Volume(yd^3) = (L X W X D)ft^3 / 27ft^3/yd^3 = (600ft X 4ft X 8ft) / 27ft^3/yd^3 = 19200ft^3 / 27ft^3/yd^3 = 711yd^3! ||| EXPLANATION: This question wants to know the volume of dirt removed from a trench in cubic yards. To start with volume is length times width times depth which will yeild volume in cubic feet. (Volume(ft^3) = (L X W X D)ft^3 = 600ft X 4ft X 8ft = 19200ft^3) All that remains is to convert cubic feet to cubic yards. since there are three feet in a yard and we are talking about a three dimensional volume one cubic yard would be equal to a volume of three feet by three feet by three feet therefore there are twenty seven cubic feet in every one cubic yard. (1yd^3 = 3ft X 3ft X 3ft => 27ft^3/yd^3) Because you want to know how many cubic yards your volume in cubic feet can be divided between, and to make the units cancel properly, you then take your volume(ft^3) and divide it by your conversion factor of twenty seven cubic feet per cubic yard. (Volume(yd^3) = Volume(ft^3) / 27ft^3/yd^3 = 19200ft^3 / 27ft^3/yd^3 = 711.11yd^3) Finally round your answer to the nearest whole cubic yard and voila. (711.1111111111yd^3 => 711yd^3!)
29.
A sedimentation tank is 80 feet long, 40 feet wide, and 16 feet deep. What is the detention time, in hours, at a flow rate of 1.8 MGD?
4.7 hours
✓
5.1 hours
✓
5.9 hours
✓
6.2 hours
✓
TLDR: DT(hrs) = (Volume(ft^3) X 7.48gal/ft^3)gal / ((Flow(MGD) X 1,000,000)gal/day / 24hrs/day)gal/hour = ((L X W X D)ft^3 X 7.48gal/ft^3)gal / (1,800,000gal/day / 24hrs/day)gal/hour = (80ft X 40ft X 16ft X 7.48gal/ft^3)gal / (1,800,000gal/day / 24hrs/day)gal/hour = 382,976gal / 75,000gal/hour = 5.1hours! ||| EXPLANATION: Our goal in this problem is to determine how many hours it will take the incoming flow to completely displace the existing volume of water in the sedimentation tank. We start by calculating the volume of the tank in cubic feet. (Volume(ft^3) = L X W X D = 80ft X 40ft X 16ft = 51,200ft^3) Then, we convert that to a volume in gallons. since it takes seven and fortyeight hundredths of a gallon to fill one cubic foot all we need to do is multiply out volume in cubic feet by the number of gallons in each cubic foot. (Volume(gal) = Volume(ft^3) X 7.48gal/ft^3 = 51,200ft^3 X 7.48gal/ft^3 = 382,976gal) Now we know the volume in gallons that need to be replaced so we can set that number asside for now and calculate how many gallons are flowing into the sedimentation basin every hour. Flow is given in millions of gallons per day (MGD or MG/D) so we start by multiplying our absolute value by one million yeilding a unit in gallons per day. (Flow(gpd) = Flow(MGD) X 1,000,000 = 1.8MGD X 1,000,000 = 1,800,000gpd) Because we need to know detention time in hours and not days however we will need to divide the number of galons we recieve in a day by the number of hours in each day. (Flow(gph) = Flow(gpd) / 24hrs/day = 1,800,000gpd / 24hrs/day = 75,000gal/hour(or gph)) We now know how many total gallons we need to replace (Volume(gal)) and the rate at which they will be replaced (Flow(gph)). What we need to do now is divide the total number of gallons by how many gallons are recieved per hour to get our detention time. (DT(hrs) = Volume(gal) / Flow(gph) = 382,976gal / 75,000gal/hour = 5.106346666 hours) Finally, we round our answer to match the choices given and BOOM! (5.106346666 hours => 5.1hrs!)
30.
A wastewater treatment plant treats 1,800,000 gallons per day, using chlorine at 10 mg/L dosage. How many pounds of chlorine are used per day?
108 pounds
✓
120 pounds
✓
150 pounds
✓
162 pounds
✓
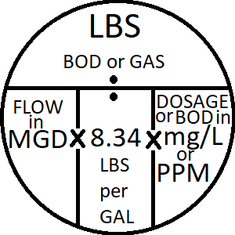
TLDR: LBS(Cl2) = Flow(MGD) X 8.34 X Dosage(mg/L) = 1.8MGD X 8.34 X 10mg/L = 150lbs! ||| NOTE: In theory this will be the first time you will have seen the mnemonic in the top left corner of the quiz so im going to explain how to use it and why it works in addition to working the example problem. EXPLANATION: To explain why the mnemonic works you have to understand that the "8.34" conversion factor is BOTH what one gallon of water weighs AND how much 1 miligram of a substance in 1 leiter of water weighs in pounds per million gallons. (1mg/L = 0.000008345... lbs/gal = 8.34 lbs/million gallons) you start by inserting the known values into the mnemonic. you are given the dosage in mg/L, 8.34 is a conversion factor, and you are given flow in gpd. since the conversion factor, and therefore the mnemonic, only works with flow given in millions of gallons per day (MGD) we need to start by converting the incoming flow from gpd to MGD by dividing it by one million so we can use it in the mnemonic. (MGD = gpd / 1,000,000 = 1,800,000gpd / 1,000,000 = 1.8MGD) The value we are looking for is how many pounds of chloring gas is used each day that means our unknown value in the mnemonic is the LBS BOD/gas in the top section. This means that we need to multiply our known values together. (LBS(Cl2 gas) = Flow(MGD) X 8.34 X Dosage(mg/L) = 1.8MGD X 8.34 X 10mg/L = 150.12lbs/day rounded to 150 lbs/day!) This equation can be reordered to find any of the missing values in ways you will see in the math section of the waste water treatment quizzes, but i'll touch on it briefly here. If the flow or dosage values had been the unknown and the pounds of gas per day used was known you would multiply your known value by 8.34 and divide the pounds per day value by that result to find your answer. (Flow(MGD) = LBS(BOD or gas) / (8.34 X dosage(mg/l or ppm which are interchangeable)) (dosage(mg/l or ppm) = LBS(BOD or gas) / (Flow(MGD) X 8.34))
Comments
No comments yet
New and Popular
Save Your Progress
Texas Basic Waste Water Ops for class D license review
Quiz series by Mandaris
Copyright H Brothers Inc, 2008–2024
Contact Us | Go To Top | View Mobile Site
