|
Integumentary
|
|
Hair
|
The two main categories for hair 1. The type that is thicker, more visible, grows longer and darker; can be found on the head, armpit, face and pubic area
2. Shorter, thinner (often called peach fuzz) found all over the body and hard to spot with the naked eye unless it's up-and-close |
Terminal hair
|
|
Vellus hair
|
The anatomy of hair 1. The visible, sensory and part that you can style 2. Tube-like structure that keeps the hair in the skin 3. Situated under the skin, accounts for hair growth |
Hair shaft
|
|
Hair follicle
|
|
Hair bulb
|
|
Keratin
|
|
This helical and fibrous protein accounts for 95% of the hair's composition
|
Keratin
|
|
Nails
|
Nails 1. The hard part of your nail you can see 2. The skin under the nail plate 3. The thin skin at the base of the nail plate 4. The root of the nail accountable for making it grow 5. The white, moon-shaped part of the nail |
Nail plate
|
|
Nail bed
|
|
Cuticle
|
|
Matrix
|
|
Lunula
|
|
Sweat Glands
|
1. The glands that secrete sweat through the skin 1.1. Sweat glands where sweat is secreted through pores 1.2. Sweat glands where sweat is secreted through the hair follicles |
Sudoriferous glands
|
|
Eccrine glands
|
|
Apocrine glands
|
|
2. Glands that produces sebum (oil) and gives the face its oil
|
Sebaceous glands
|
|
3. Glands situated in the ears that secrete the ear wax
|
Ceruminous glands
|
|
4. The glands situated in the person chest, and for women, they'll produce milk port-partum
|
Mammary glands
|
|
|
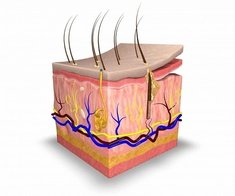
Skin
|
|
The skin is the body's largest _____
|
Organ
|
The three layers of the skin 1. The thinnest outer layer; visible and can be touched, consists of cells, waterproof barrier 2. The middle and thickest layer; contains sweat and oil glands and hair follicles 3. The fatty bottom layer; helps insulate the body |
Epidermis
|
|
Dermis
|
|
Hypodermis / Subcutaneous
|
|
Epidermis
|
The five layers of the Epidermis 1. Deepest layer; where new skin cells develop, contains keratino-and melanocytes 2. Mostly consists of keratinocytes, helps making the skin flexible and strong 3. The third layer, consisting of keratinocytes 4. A thin, transparent layer of keratinocytes that are becoming less round have a flatter shape 5. The visible top layer of the epidermis, the layer where keratinocytes becomes corneocytes |
Stratum Basale
|
|
Stratum Spinosum
|
|
Stratum Granulosum
|
|
Stratum Lucidum
|
|
Stratum Corneum
|
Functions
1. The outermost layer of the epidermis (corneum) holds in water in order to keep the skin... 2. The bottom layer will develop skin cells 3. Acts as a barrier from impact and also pathogens and radiation 4. Determining the race of the person |
Hydration
|
|
Production
|
|
Protection
|
|
Skin Colour
|
The three cells of the Epidermis 1. Cells that produce Keratin; the main component of the entire layer 2. Cells that produce Melanin; a substance that determines the skin colour 3. Cells that prevent things from breaching the skin |
Keratinocytes
|
|
Melanocytes
|
|
Langerhans cells
|
The two types of Melanin that melanocytes produce 1. Melanin for hair, skin and eyes 2. Melanin for lips, nipples, genitals and the glans |
Eumelanin
|
|
Pheomelanin
|
|
Strong, dead keratinocytes that protect the body from harm, including abrasions, light, heat and pathogens
|
Corneocytes
|
|
Dermis
|
The two layers of the Dermis 1. The bottom layer of the dermis; thick and contains blood vessels 2. Top layer of the dermis, much thinner, interlocks with the bottom layer of the epidermis |
Reticular dermis
|
|
Papillary dermis
|
|
Hypodermis
|
Functions
1. _______ the dermis to the muscles and bones 2. _________ the body to protect from the cold, and also secrete sweat to prevent overheating 3. Allows skin to move withut rubbing against muscles and bones, and also _______ the organs by acting as a shock absorber 4. Stores ______ for later use |
Connects
|
|
Protect
|
|
Insulates
|
|
Energy
|
The two things that make up the majority of the hypodermis
1. Fatty tissue, producing fat cells 2. Made up of collagen and elastin (proteins), connects all structures in the body |
Adipose tissue
|
|
Connective Tissue
|
|