Featured Quizzes
User Quizzes
Create Quiz
Data and Charts
Badges and Games
About JetPunk
JetPunk Shop
Dark Mode
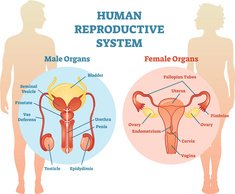
General Medicine: Reproductive systems
How well do you know the two reproductive systems?
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/9117-male-reproductive-system
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/9118-female-reproductive-system
Rate:
Last updated: January 7, 2024
You have not attempted this quiz yet.
More quiz info >>
| First submitted | January 7, 2024 |
| Times taken | 36 |
| Average score | 22.6% | Report this quiz | Report |
30:00
Enter answer here
0
/ 53 guessed
Time Used
00:00
Best Time
00:00
The quiz is paused. You have remaining.
Scoring
You scored / = %
This beats or equals
% of test takers
also scored 100%
The average score is
Your high score is
Your fastest time is
Keep scrolling down for answers and more stats ...
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Comments
No comments yet
New and Popular
Save Your Progress
Medicine
Quiz series by Jakovlev
...
Copyright H Brothers Inc, 2008–2024
Contact Us | Go To Top | View Mobile Site
