Featured Quizzes
User Quizzes
Create Quiz
Data and Charts
Badges and Games
About JetPunk
JetPunk Shop
Dark Mode

pharmacology - multi choice mid sem practice exam
Concepts and terminology, concentration response relationships, ligand receptor interactions, agonism & antagonism, drug administration, drug absorption, drug distribution, Drug Metabolism and Elimination, PK-PD, Dose-Finding Studies, Drug Registration and Scheduling, Sympathetic nervous system, Parasympathetic nervous system, Nicotinic drugs, inotropes and vasodilators, antiarrhythmics, renal drugs
Rate:
Last updated: May 26, 2023
You have not attempted this quiz yet.
More quiz info >>
| First submitted | April 4, 2023 |
| Times taken | 61 |
| Average score | 40.3% | Report this quiz | Report |
60:00
The quiz is paused. You have remaining.
Scoring
You scored / = %
This beats or equals
% of test takers
also scored 100%
The average score is
Your high score is
Your fastest time is
Keep scrolling down for answers and more stats ...
1.
Drug A has a lower potency and a lower efficacy than drug B. Therefore drug A is:
An inverse agonist
✓
An antagonist
✓
A partial agonist
✓
A full agonist
✓
2.
The –olol ending in a drug name denotes that the drug belongs to which drug class?
Beta adrenergic blocker
✓
Proton pump inhibitor
✓
Alpha adrenergic blocker
✓
H2 receptor antagonist
✓
3.
Which of the following is classed as a parenteral route of drug administration?
Sublingual
✓
Rectal
✓
Oral
✓
Subcutaneous
✓
4.
Which of the following is not observed in Type II diabetes mellitus:
Late onset
✓
Unresponsive to treatment with oral hypoglycaemic drugs
✓
Obesity usually present
✓
Ketosis resistant
✓
5.
When phenobarbitone reduces the anticoagulant effect of warfarin by accelerating its hepatic metabolism, it is acting as a:
Pharmacokinetic inhibitor
✓
Chemical inhibitor
✓
Competitive inhibitor
✓
Physiological inhibitor
✓
6.
One of the effects of sympathetic nervous system stimulation, is urinary retention due to adrenaline-mediated bladder sphincter contraction. Which adrenergic receptor subtype is activated in this process?
Beta 2
✓
Alpha 1
✓
Alpha 2
✓
Beta 1
✓
7.
Myasthenia Gravis is an autoimmune condition that targets acetylcholine receptors on the neuromuscular junction. Neostigmine is an effective treatment for this condition. Neostigmine is:
A cholinesterase activator
✓
A cholinergic agonist
✓
A cholinergic antagonist
✓
A cholinesterase inhibitor
✓
8.
Angiotensin II receptor blockers are useful drugs in the treatment of hypertension. Which of the following is an example of this class of drugs?
Irbesartan
✓
Amlodipine
✓
Perindopril
✓
Atenolol
✓
9.
Frusemide is an example of:
Potassium sparing diuretic
✓
Osmotic diuretic
✓
Thiazide diuretic
✓
Loop diuretic
✓
10.
Which of the following is an antagonist at the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor?
Atropine
✓
Nicotine
✓
d-Tubocurarine
✓
Muscarine
✓
11.
A 55-year-old woman with heart failure is to be treated with a diuretic drug. Drugs X and Y have the same mechanism of diuretic action. Drug X in a dose of 5 mg produces the same magnitude of diuresis as 500 mg of drug Y. This suggests that:
Drug X is about 100 times more potent than drug Y
✓
Drug X will have a shorter duration of action than drug Y because less of drug is present for a given effect
✓
Drug X is a safer drug than drug Y
✓
Drug X is less efficacious than drug Y
✓
Toxicity of drug X is less than that of drug Y
✓
12.
In the absence of other drugs, pindolol causes an increase in heart rate by activating beta adrenergic receptors. In the presence of highly effective beta receptor agonists, however, pindolol causes a dose-dependent, reversible decrease in heart rate. Therefore, pindolol is classed as:
A physiological antagonist
✓
An irreversible antagonist
✓
A partial agonist
✓
A chemical antagonist
✓
13.
Heroin is usually measured in 25 mg bags. Unsuspecting users of China White who normally use three bags of heroin to get a ‘high’ died after injecting one bag of China White. If 50% of China White users died after injecting one bag, which of the following statements is correct?
The ED50 for China White is 25 mg
✓
Heroin is more potent than China White
✓
The therapeutic index for China White is larger than that for heroin
✓
The LD50 for China White is 25 mg
✓
14.
For a partial agonist, which of the following is true?
Need few receptors occupied to get maximal response
✓
Need few receptors occupied to get non-maximal response
✓
Need all receptors occupied to get maximal response
✓
Need all receptors occupied to get non-maximal response
✓
15.
Assays to look at dose-effect interactions reveal which of the following?
Emax, Kd
✓
Bmax, ED50
✓
Emax, ED50
✓
Bmax,Kd
✓
16.
The –profen ending in a drug name denotes that the drug belongs to which drug class?
Proton pump inhibitor
✓
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID)
✓
Beta adrenergic blocker
✓
H2 receptor antagonist
✓
17.
Which of the following receptor sub-groups elicits the fastest response when activated by an agonist?
Ligand-gated ion channels (e.g. nicotinic acetylcholine receptor)
✓
Nuclear receptors (e.g. oestrogen receptors)
✓
G protein-coupled receptors (e.g. muscarinic acetylcholine receptor)
✓
Kinase-linked receptors (e.g. insulin receptor)
✓
18.
In the Langmuir equation, Ntot-N denotes:
The number of unoccupied receptors in a tissue after addition of drug
✓
The total number of receptors in a tissue
✓
The concentration of the drug added to a tissue
✓
The number of receptors in a tissue occupied by the drug
✓
19.
When verapamil & nifedipine prevent the influx of calcium ions specifically blocking the contraction of smooth muscle produced by other drugs, they are acting as:
Pharmacokinetic inhibitors
✓
Non-competitive inhibitors
✓
Chemical inhibitors
✓
Competitive inhibitors
✓
20.
One of the effects of sympathetic nervous system stimulation, is blood vessel vasodilation. Which adrenergic receptor subtype is activated in this process?
Alpha 1
✓
Beta 2
✓
Alpha 2
✓
Beta 1
✓
21.
Atropine is an effective treatment for the relief of ciliary spasm. Atropine is:
A cholinesterase inhibitor
✓
A cholinergic agonist
✓
A cholinergic antagonist
✓
A cholinesterase activator
✓
22.
ACE inhibitors are useful drugs in the treatment of hypertension. Which of the following is an example of this class of drugs?
Amlodipine
✓
Propranolol
✓
Captopril
✓
Candesartan
✓
23.
Angiotensin II receptor blockers are useful drugs in the treatment of hypertension. Which of the following is an example of this class of drugs?
Propranolol
✓
Enalopril
✓
Amlodipine
✓
Irbesartan
✓
24.
Which of the following is an agonist at the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor?
d-Tubocurarine
✓
Nicotine
✓
Muscarine
✓
Atropine
✓
25.
Which of the following is an antagonist at the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor?
Nicotine
✓
Atropine
✓
d-Tubocurarine
✓
Muscarine
✓
26.
If drug A has an ED50 of 5mM, drug B has an ED50 of 50mM and drug C has an ED50 of 500mM, which drug is the most potent?
Drug A
✓
You cannot determine the potency from ED50 values
✓
Drug B
✓
Drug C
✓
27.
Two antihypertensive drugs, X and Y, were studied in a large group of patients and the percentages of the group showing a specific therapeutic effect (20 mm Hg decrease in systolic blood pressure) were determined. The results are shown in the table below.
Which of the following statements about these results, from the information provided, is correct?
The 2 drugs act on the same receptors
✓
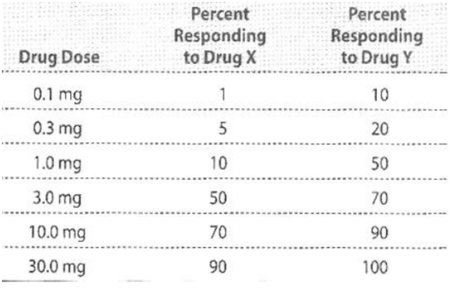 ✓
✓
Drug Y is more effective than drug X
✓
The therapeutic index of drug Y is 10
✓
Drug X is safer than drug Y
✓
Drug X is less potent than drug Y
✓
28.
Which of the statements below is true with regards to ethanol?
Ethanol has high chemical and high biological specificities
✓
Ethanol has high chemical and low biological specificities
✓
Ethanol has low chemical and low biological specificities
✓
Ethanol has low chemical and high biological specificities
✓
29.
With respect to the harmful effects of drugs, which of the following statements is false?
An increase in the sensitivity of a drug in susceptible patients, leads to a decrease in the margin of safety for that particular drug
✓
Contact dermatitis can result from an allergic reaction to a drug
✓
The placenta acts as a barrier preventing all drugs taken by the mother from affecting the developing foetus
✓
Drugs taken by a lactating woman can be secreted in the breast milk
✓
30.
Which cellular compound does the phosphodiesterase enzyme family produce from cyclic AMP?
ATP
✓
ADP
✓
AMP
✓
Cyclic ADP
✓
31.
The levels of which ion directly increase as a result of digitalis action on the cardiac myocyte?
Sodium
✓
Chloride
✓
Potassium
✓
Fluoride
✓
The inhibition of the sodium-potassium ATPase by digitalis leads to an increase in intracellular sodium levels, which then leads to a decrease in the activity of the sodium-calcium exchanger. This ultimately results in an increase in intracellular calcium levels, leading to the positive inotropic effect of digitalis on the cardiac myocyte.
32.
Assuming complete absorption and an elimination half-life of 5 hours, how many mg of a drug will remain in the body 35 hours after administering a 400 mg dose?
12.5
✓
6.25
✓
3.125
✓
25
✓
Amount of drug remaining = Initial dose x (1/2)^(time elapsed / half-life) Amount of drug remaining = 400 mg x (1/2)^(35/5) = 400 mg x 0.0078125 = 3.125 mg
33.
If 500mg of a drug is administered orally and 50mg is absorbed unchanged, the bioavailability of the drug is:
10%
✓
100%
✓
25%
✓
50%
✓
Bioavailability = (Amount of drug absorbed / Amount of drug administered) x 100% Bioavailability = (50mg / 500mg) x 100% Bioavailability = 10%
34.
Which of the following is a beta adrenergic blocker used in the treatment of angina pectoris?
Glycerol trinitrate
✓
Dobutamine
✓
Atenolol
✓
Diltiazem
✓
35.
How do angiotensin receptor blockers affect the production of aldosterone?
First they inhibit then stimulate aldosterone production
✓
They have no effect on aldosterone production
✓
They inhibit production of aldosterone
✓
They stimulate production of aldosterone
✓
36.
A drug has an elimination rate constant of 0.355 hr-1. Its elimination half-life is:
1.95 hours
✓
4.95 hours
✓
3.95hours
✓
2.95 hours
✓
37.
If 550 mg of a drug are administered intravenously and the resultant drug plasma concentration is determined to be 25 μg/100mL, what is the apparent volume of distribution of the drug?
22L
✓
22000L
✓
2200L
✓
220L
✓
The formula to calculate the apparent volume of distribution is: Vd = (amount of drug administered) / (plasma drug concentration) Converting the units of amount of drug administered to grams: 550 mg = 0.55 g Substituting the values into the formula: Vd = 0.55 g / (25 μg/100mL) Converting the units of plasma drug concentration to grams per liter (g/L): 25 μg/100mL = 0.25 mg/L = 0.00025 g/L Substituting this value into the formula: Vd = 0.55 g / (0.00025 g/L) Vd = 2200 L Therefore, the apparent volume of distribution of the drug is 2200L.
38.
Arrange these in order of which elicits a faster response when activated by an agonist (fastest to slowest):
a. Ligand-gated ion channels (e.g. nicotinic acetylcholine receptor)
b. Kinase-linked receptors (e.g. insulin receptor)
c. Nuclear receptors (e.g. oestrogen receptors)
d. G protein-coupled receptors (e.g. muscarinic acetylcholine receptor)
d, b, a, c
✓
a, d, b, c
✓
a, b, c, d
✓
d, c, b, a
✓
39.
What is the plasma concentration of a drug when 700 mg is given by IV bolus to a 220lb patient if her volume of distribution is 35 L/kg. (Please note that 1kg = 2.2lb)
0.2mg/L
✓
0.1mg/L
✓
0.5mg/L
✓
1mg/L
✓
First, we need to convert the patient's weight to kg: 220 lb ÷ 2.2 lb/kg = 100 kg Next, we can calculate the total dose of the drug in mg/kg: 700 mg ÷ 100 kg = 7 mg/kg Then, we can use the volume of distribution to calculate the expected plasma concentration: Plasma concentration = Total dose / Volume of distribution Plasma concentration = 7 mg/kg / 35 L/kg Plasma concentration = 0.2 mg/L.
40.
The area under the serum concentration-time curves (AUC) were measured after single doses of 10 mg of a new antihypertensive drug were administered in hypertensive patients. The results were as follows: intravenous bolus AUC = 2500 mg . h/L, oral capsule AUC = 500 mg . h/L, oral liquid AUC = 650 mg . h/L. What is the bioavailability of the oral liquid?
0.26 or 26%
✓
0.2 or 20%
✓
0.29 or 29%
✓
0.23 or 23%
✓
Bioavailability = (AUC oral / dose oral) / (AUC IV / dose IV) Bioavailability = (650 mg . h/L / 10 mg) / (2500 mg . h/L / 10 mg) Bioavailability = 65 / 250 Bioavailability = 0.26 or 26%
41.
In the absence of other drugs, pindolol causes an increase in heart rate by activating beta adrenergic receptors. In the presence of highly effective beta receptor agonists, however, pindolol causes a dose-dependent, reversible decrease in heart rate. Therefore, pindolol is:
A chemical antagonist
✓
An irreversible antagonist
✓
A partial agonist
✓
A spare receptor agonist
✓
42.
A 70 year old hypertensive man with a childhood history of asthma had a recent myocardial infarction and is prescribed metoprolol. Which class of drug does metoprolol belong to?
Beta 2 adrenergic receptor antagonist
✓
Beta 1 adrenergic receptor agonist
✓
Beta 1 adrenergic receptor antagonist
✓
Beta 2 adrenergic receptor agonist
✓
43.
Which of the following is an anorexiant used in the treatment of obesity?
Orlistat
✓
Phentermine
✓
Tetracycline
✓
Glucagon
✓
Phentermine is an anorexiant used in the treatment of obesity. The other options are not used for this purpose. Orlistat is a lipase inhibitor used to treat obesity, tetracycline is an antibiotic, and glucagon is a hormone used to treat severe hypoglycemia.
44.
A particular illness or disease state in which a drug has been shown to have a therapeutic effect is known as:
A contra-indication
✓
An indication
✓
A precaution
✓
An interaction
✓
45.
When an antagonist interacts with a G protein coupled receptor, what is the effect of the drug on the GTPase activity of the G protein linked to that receptor.
It stops the GTPase activity completely
✓
It slows down the GTPase activity
✓
It has no effect on the GTPase activity
✓
It speeds up the GTPase activity
✓
46.
Which of the following is false for the stimulatory G protein Gs?
It is ADP-ribosylated by the exotoxin secreted by Bordetella pertussis
✓
It is found on the inner leaflet of the cell plasma membrane
✓
It is linked to the beta 2 adrenergic receptor
✓
It causes in an increase in intracellular cyclic AMP when stimulated
✓
47.
Which of the following is classed as a parenteral route of drug administration?
Oral administration
✓
Intravenous administration
✓
Inhalation
✓
Sublingual
✓
48.
With respect to the pharmacokinetic properties of morphine, which of the following is true:
Morphine is highly lipid soluble and as such easily crosses the blood-brain barrier
✓
Morphine salts have poor oral bioavailability as they undergo extensive first- pass metabolism in the liver
✓
About 10% of a morphine dose is excreted in the urine as morphine or its metabolites within the first 24 hours after administration
✓
Morphine salts are poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract
✓
49.
The amount of a drug given initially to obtain the desired plasma concentration as soon as possible is known as:
The maintenance dose
✓
The initial dose
✓
The therapeutic dose
✓
The loading dose
✓
50.
Which phase in drug development does post-marketing surveillance occur?
Phase IV
✓
Phase V
✓
Phase II
✓
Phase III
✓
51.
Which of the schedule levels indicates the entry level for a prescription-only medicine?
Schedule 4
✓
Schedule 2
✓
Schedule 8
✓
Schedule 6
✓
52.
Prazosin, a common vasodilator, belongs to which drug class?
Alpha 2 adrenergic receptor agonist
✓
Alpha 2 adrenergic receptor antagonist
✓
Alpha 1 adrenergic receptor antagonist
✓
Alpha 1 adrenergic receptor agonist
✓
53.
Inhibition of the parasympathetic nervous system with an antimuscarinic agent such as tropicamide, results in which of the following adverse effects?
Salivation
✓
Sweating
✓
Urinary retention
✓
Diarrhoea
✓
54.
Calcium channel blockers such as diltiazem belong to which class of antiarrhythmic drugs used in the treatment of tachyarrhythmias?
Class IV
✓
Class II
✓
Class I
✓
Class III
✓
55.
Drug F reduced the basal GTPase activity in a concentration dependent manner. What should Drug F be classified as?
Antagonist
✓
Inverse agonist
✓
Partial agonist
✓
Agonist
✓
56.
Drug D reduces the anticoagulant effect of Drug F by accelerating its hepatic metabolism. What should Drug D be classified as?
Non-competitive antagonist
✓
Competitive antagonist
✓
Pharmacokinetic antagonist
✓
Inverse agonist
✓
57.
A single intravenous dose of 40 mg of diazepam was administered to a patient. A blood sample was drawn and it contained 50 µg/mL. Calculate the apparent volume of distribution for the drug.
0.02 L
✓
0.8 L
✓
8 L
✓
0.08 L
✓
58.
Drug J raises the arterial blood pressure acting on heart and peripheral vessels whilst Drug K lowers arterial blood pressure causing vasodilation Therefore, Drug K can be classified as:
Physiological antagonist
✓
Chemical antagonist
✓
Competitive antagonist
✓
Non-competitive antagonist
✓
59.
Systemic distribution of many drugs can evoke skin reactions that are a result of an immunological reaction, generally caused by photosensitization of the drug. What type of adverse effects would this be considered as?
Cardiovascular reactions
✓
Gastrointestinal reactions
✓
Neurological reactions
✓
Cutaneous reactions
✓
60.
Assuming complete absorption and an elimination half-life of 5 hours, how many mg of a drug will remain in the body 35 hours after administering a 400 mg dose?
6.2 mg
✓
12.4 mg
✓
25 mg
✓
3.1 mg
✓
Amount remaining = Initial dose x (0.5)^(time elapsed / half-life) Plugging in the values given: Amount remaining = 400 mg x (0.5)^(35 hours / 5 hours) Amount remaining = 400 mg x (0.5)^7 Amount remaining = 400 mg x 0.0078125 Amount remaining = ~3.1 mg
61.
What is the plasma concentration of a drug when 700 mg is given by IV bolus to a 220lb patient if her volume of distribution is 3.5L/kg. (Please note that 1kg = 2.2lb)
2 mg/L
✓
0.5 mg/L
✓
1 mg/L
✓
4 mg/L
✓
First, we need to convert the patient's weight from pounds to kilograms: 220 lb ÷ 2.2 = 100 kg Next, we can use the formula for calculating plasma concentration: Plasma concentration = Amount of drug administered / Volume of distribution Plasma concentration = 700 mg / (3.5 L/kg x 100 kg) = 2 mg/L Therefore, the plasma concentration of the drug is 2 mg/L.
62.
Drug B is given to a rat and the maximal response is at 100. Drug C is given to the same rat and the maximal response has diminished. Drug A is further given at higher doses but response doesn’t change. What should Drug C be classified as?
Irreversible competitive antagonist
✓
Non-competitive antagonist
✓
Partial agonist
✓
Reversible competitive antagonist
✓
No comments yet
New and Popular
Save Your Progress
Human Pharmacology
Quiz series by camisadorising
...
Copyright H Brothers Inc, 2008–2024
Contact Us | Go To Top | View Mobile Site
